Issue #103 - LEGAL-BERT: The Muppets straight out of Law School

Introduction
BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) is a large-scale pre-trained autoencoding language model that has made a substantial contribution to natural language processing (NLP) and has been studied as a potentially promising way to further improve neural machine translation (NMT).
“Given that BERT is based on a similar approach to neural MT in Transformers, there’s considerable interest and research into how the two can be combined” — Dr. John Tinsley, Co-founder and CEO, Iconic Translation Machines
But, there has been limited investigation on its adaptation guidelines in specialised domains. In this post, we will discuss the systematic investigation of the available strategies when applying BERT in specialised domains as proposed by Chalkidis et. al., (2020).
About Legal Domain
Legal text (e.g., laws, court pleadings, contracts) has distinct characteristics compared to generic corpora. The recognizable characteristics include specialised vocabulary, particularly formal syntax, semantics based on extensive domain-specific knowledge etc., to the extent that legal language is often classified as a ‘sublanguage’.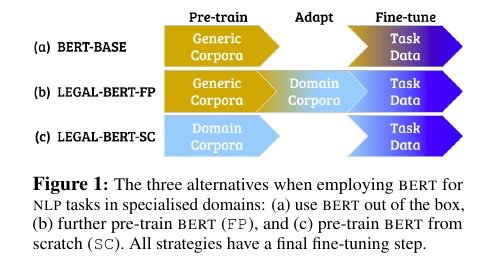 BERT can be pre-trained on a massive corpus of data, and then fine-tuned to a task for which you have a limited amount of data. This allows BERT to provide a significantly higher performance than models that are only able to leverage a small task-specific dataset. Chalkidis et. al., (2020) systematically explore the following strategies for BERT adaptation in the legal domain :
BERT can be pre-trained on a massive corpus of data, and then fine-tuned to a task for which you have a limited amount of data. This allows BERT to provide a significantly higher performance than models that are only able to leverage a small task-specific dataset. Chalkidis et. al., (2020) systematically explore the following strategies for BERT adaptation in the legal domain :
(a) use out of the box pre-trained BERT (BERT-BASE) (b) further pre-train (FP) BERT-BASE on domain-specific corpora (LEGAL-BERT-FP) (c) pre-train BERT from scratch (SC) on domain specific corpora with a new vocabulary of sub-word units (LEGAL-BERT-SC) (d) pre-train a smaller light-weight version of LEGAL-BERT-SC with fewer parameters (LEGAL-BERT-SMALL)
Key Findings
- Further pre-training (FP) or pre-training BERT from scratch (SC) on in-domain data produces better results than BERT-BASE for domain-specific tasks.
- This paper presents an expanded grid search compared to the guidelines of Devlin et. al., (2019) for fine-tuning BERT, that has a significant impact on performance.
- From the results, LEGAL-BERT-SMALL is comparable to LEGAL-BERT (SC and FP) across most datasets while the training time for small models is 4 times faster and requires fewer hardware resources than the LEGAL-BERT.

