Issue #110 - Better Out of Vocabulary Translation with Bilingual Terminology Mining

Introduction
A significant weakness in conventional neural machine translation (NMT) systems is their inability to correctly translate Out of Vocabulary (OOV) words: end-to-end NMTs tend to have relatively small vocabularies due to memory limitations with a single “unknown token” (usually abbreviated in MT slang as “unk”) that represents every possible out-of-vocabulary (OOV) word. In NMT, byte-pair encoding can be used to represent OOVs, but they are still often incorrectly translated. In today’s blog post, we take a look at the mining procedure proposed in “Better OOV Translation with Bilingual Terminology Mining” (Huck et al., 2019).
The paper proposes a simple approach for improving the translation of OOVs using bilingual word embeddings (BWEs). BWEs represent source and target language words in a joint space and can be built by using easy-to-obtain monolingual data.
Proposed Approach
The paper proposes the use of simple-to-construct BWEs to translate the OOVs.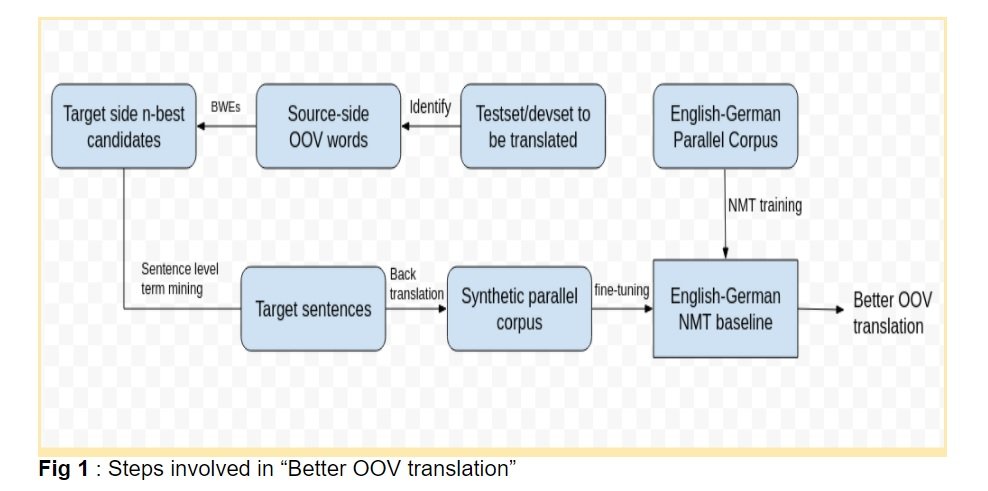 As a first step, the source language words, in text to be translated, which are not included in the parallel training data are identified (OOVs). The BWEs are constructed using topic specific monolingual data from the target language and are used to translate the OOVs by taking n-best translations. The n-best candidates are then used to mine all the sentences that contain any of those from the monolingual data. This set of target side sentences are then back-translated to generate the synthetic parallel corpus. To improve the OOV translation, the baseline NMT system is fine-tuned on the generated parallel corpus for only one training step, as in Farajian et al. (2017, 2018).
As a first step, the source language words, in text to be translated, which are not included in the parallel training data are identified (OOVs). The BWEs are constructed using topic specific monolingual data from the target language and are used to translate the OOVs by taking n-best translations. The n-best candidates are then used to mine all the sentences that contain any of those from the monolingual data. This set of target side sentences are then back-translated to generate the synthetic parallel corpus. To improve the OOV translation, the baseline NMT system is fine-tuned on the generated parallel corpus for only one training step, as in Farajian et al. (2017, 2018).
Experimentation
The Europarl v7 (EU) English to German parallel dataset containing 1.9M sentence pairs (Philipp Koehn, 2005) is used to train the baseline NMT system. The experimentation involves translation of English to German medical domain sentences. To ensure good quality, the BWEs are trained on both the medical domain data ( UFAL Medical Corpus ) and Europarl data.Training BWEs
The monolingual data on both the source and target side is processed individually using fastText’s skipgram model to obtain the monolingual embeddings. The MUSE’s implementation of training unsupervised BWEs is used on the monolingual embeddings to obtain BWE based source-target dictionaries.Term-mining using BWEs
The BWE based dictionaries are used to translate the OOVs in the testset, taking the 5-best candidates into account. The 5-best candidates are obtained based on the cosine and orthographic similarity measures. These 5-best candidates for each OOV word are used to mine sentences from target-side monolingual data. All the mined sentences are then back-translated using a German-English baseline engine to produce the synthetic parallel corpus.NMT Fine-Tuning
Both the dictionary based translation and sentence mining are handled at the word level. To improve the OOV translation, the English-German Baseline engine is fine-tuned using generated synthetic corpus. The model is trained for only one training step, similar to Farajian et al. (2017, 2018), to ensure that the previously gained knowledge is not overwritten and the NMT system learns newly seen words at the same time.Results
Fig 2. shows some example translations where the baseline system fails to produce a correct translation but the fine-tuned model gives the correct translation for a given sentence. The evaluation results are presented in case-sensitive BLEU scores.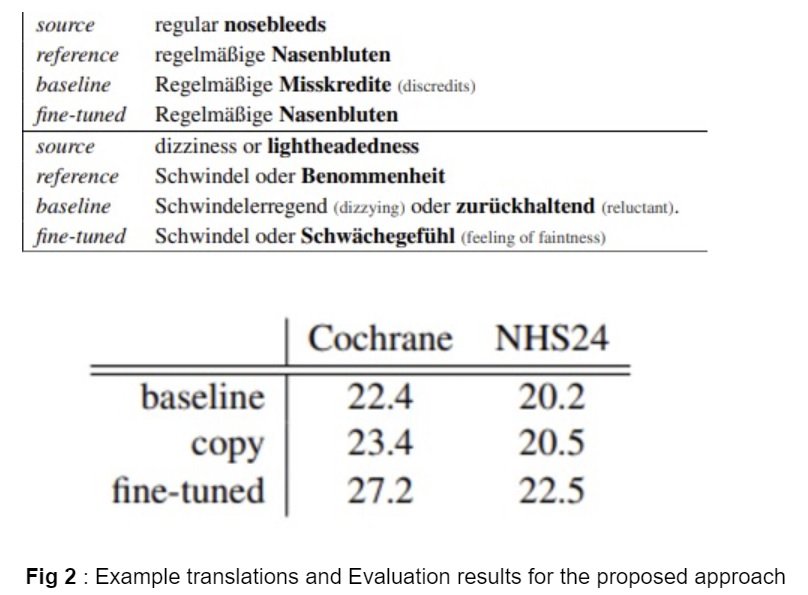 The approach is compared with a simple OOV token copying strategy (the OOV token on the source side is copied to the target) and it can be seen that the token copying strategy results in an improvement but not by a large margin. The fine tuned system, by contrast, performs considerably better, achieving an increase of +4.8 and +2.3 BLEU points.
The approach is compared with a simple OOV token copying strategy (the OOV token on the source side is copied to the target) and it can be seen that the token copying strategy results in an improvement but not by a large margin. The fine tuned system, by contrast, performs considerably better, achieving an increase of +4.8 and +2.3 BLEU points.

