Issue #94 - Unsupervised Parallel Sentence Extraction with Parallel Segment Detection Helps Machine Translation

Introduction
Curating corpora of quality sentence pairs is a fundamental task to building Machine Translation (MT) systems. This resource can be availed from Translation Memory (TM) systems where the human translations are recorded. However, in most cases we don’t have TM databases but comparable corpora, e.g. news articles of the same story in different languages. In this post, we review an unsupervised parallel sentence extraction method based on bilingual word embeddings (BWEs) by Hangya and Fraser (2019).
Parallel Segment Detection Using Bilingual Word Embeddings
Word embeddings are used to represent the meaning of a word in a multidimensional space where words with similar meanings will appear nearby to each other. A great insight on this technology is that the space can be shared across languages, and so it could be useful in many tasks in MT. The recent developments in unsupervised bilingual word embeddings (BWEs) even enabled the building of MT systems using only monolingual corpora, Lample et al. (2018).
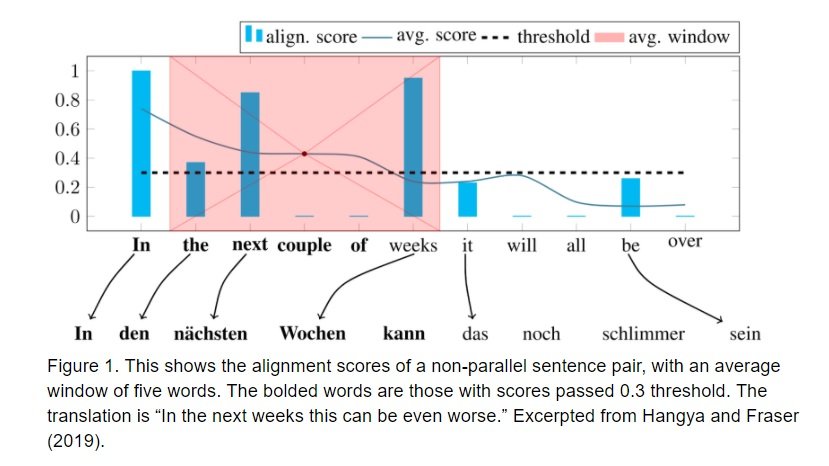
Fig. 1 shows an example of the approach by Hangya and Fraser (2019). The idea is to calculate the similarity of the two sentences from different languages and extract them as parallel if the similarity score passes the threshold. The authors use MUSE to build unsupervised BWEs, which is then used to calculate the similarity between two words using the Cross-Domain Similarity Local Scaling (CSLS) metric. For each source language word, a dictionary of its nearest 100 words (in target language) is created using CSLS.
To detect parallel “segments” in a sentence pair, the method used “calculates sentence similarity by averaging the scores of the most similar words” with the aim to reduce computation complexity. The algorithm is depicted with a non-parallel sentence pair in Fig. 1. In the final stage, the score of a sentence pair is the average word alignment score which is multiplied by the ratio of lengths of longest parallel segments over the whole sentence. Then the sentence pairs with scores larger than the threshold are chosen as parallel sentences.